#1 out of 2282.0K est. views0.00%
science18h ago
DNA study provides 'almost perfect correlation' for first Australians' arrival
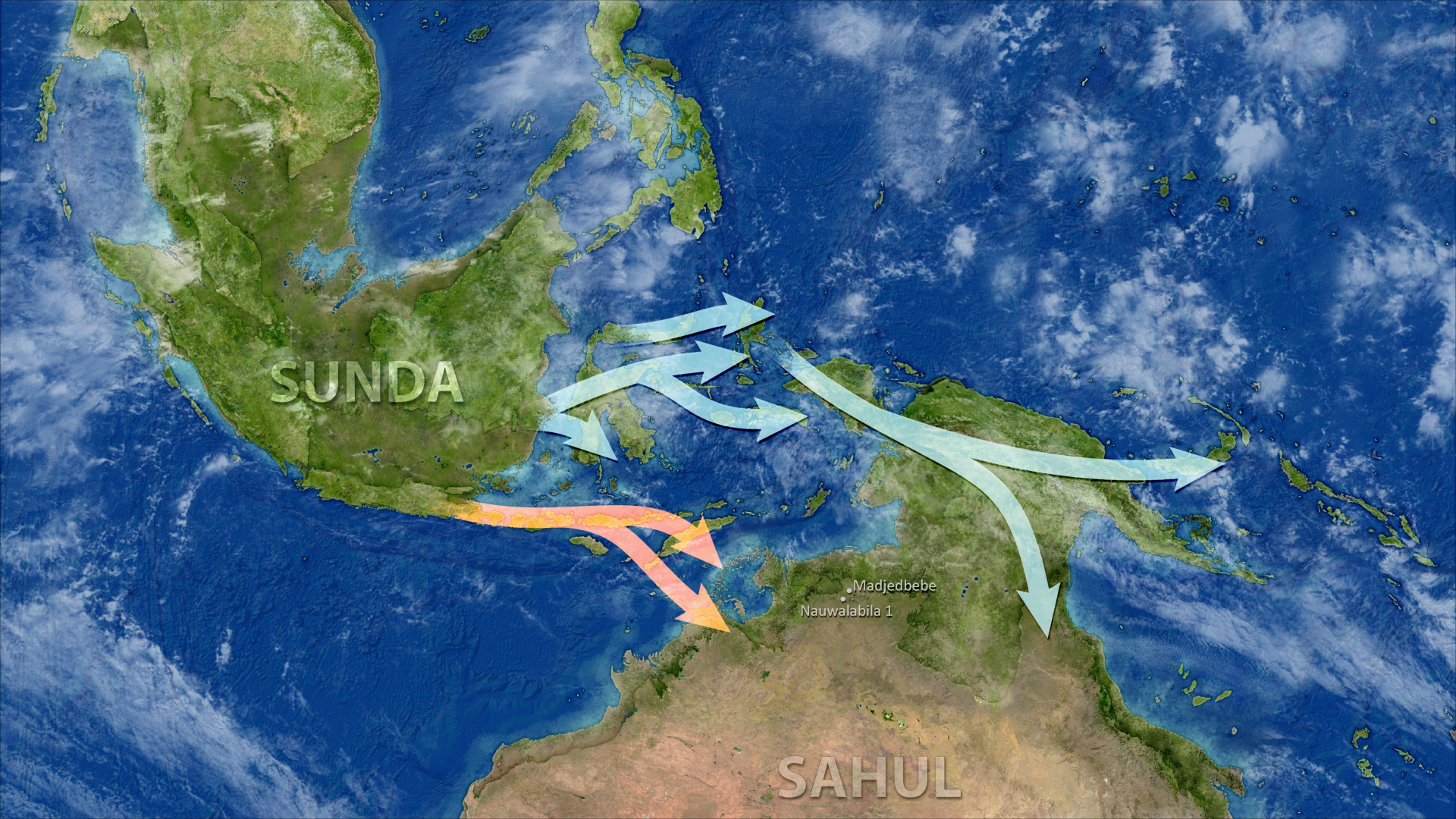
- A new genetic study places the first Australians in Sahul about 60,000 years ago via two routes, narrowing the gap with archaeology.
- The study analyzed 2,456 mitochondrial DNA samples and used a correction curve to adjust mutation rates.
- Researchers say the findings help reconcile genetic dates with the archaeological record, which includes sites about 65,000 years old.
- Archaeologists say the arrival timeline aligns with past rock shelter excavations, supporting a long Aboriginal heritage.
- Some scientists remain cautious, noting that more genome-wide work is needed to confirm the genetic timeline.
- The two dispersals are dated to roughly 60,000 years ago, suggesting early seafaring and boat use.
- The study analyzed genetic data from Indigenous Australians and New Guineans to test mutation rates across groups.
- Scientists acknowledge the debate on the exact date between genetic and archaeological evidence is ongoing.
- The Madjedbebe site in the Northern Territory remains a key reference point for early Australian occupation dating to about 65,000 years.
- The research involved collaboration among archaeologists and geneticists to link seafaring timing with climate and routes.
- Experts emphasize a deep heritage for Indigenous communities and the ongoing importance of further discoveries.
Vote 1